BONE GRAFTS
Bone grafting is a surgical procedure that replaces missing bone and provides a scaffold for new bone growth. Bone grafts may be autograft (obtained from the patient’s body), allograft (obtained from a donor), or synthetic.
LEARN MORE
Benefits of using allograft/synthetic versus autograft include:
- Eliminates the need for a second surgical site
- Reduced pain and loss of function from the second surgical site
- Reduced surgical time
- Reduced risk of infection or bleeding
- Reduced recovery time after surgery
Successful bone grafts have one or more of these three properties:
- Osteoconductive: graft acts as a scaffold for the growth of natural bone
- Osteoinductive: graft contains growth factors that recruit immature cells and stimulate those cells to develop into active bone-forming cells called osteoblasts
- Osteogenic: graft directly provides living cells that contribute to the growth of natural bone

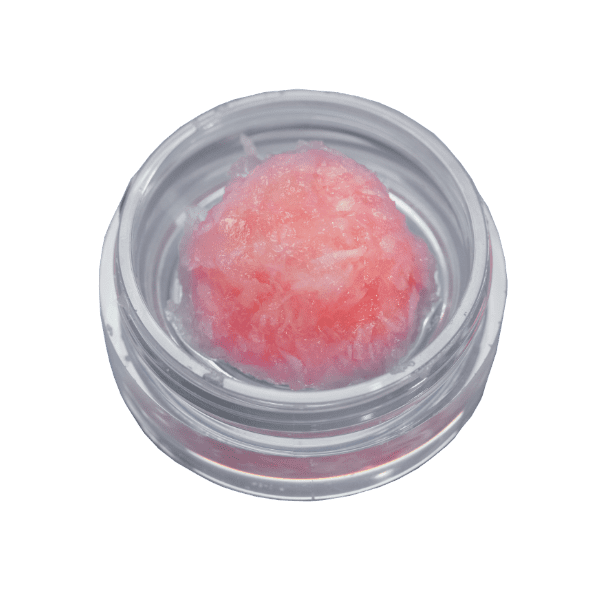
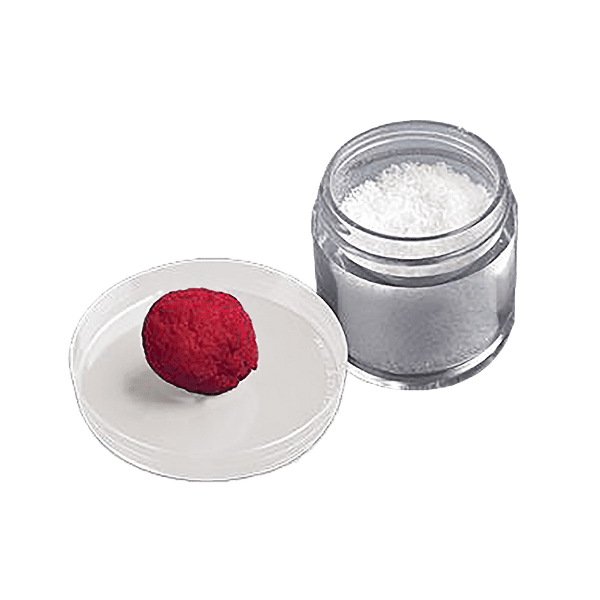
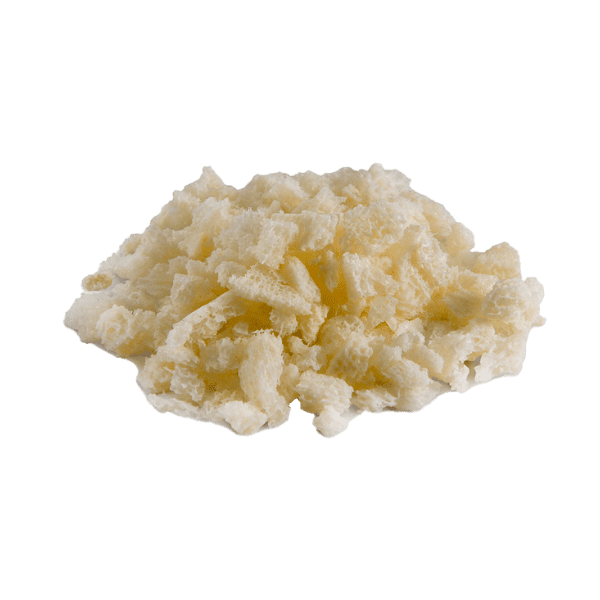
EnduriFuse is allograft bone containing viable bone-derived cells. This innovative graft contains properties ideal for the growth of natural bone:
- An osteoconductive three-dimensional scaffold with cortical and cancellous components
- A demineralized bone scaffold with osteoinductive potential containing growth factors that recruit immature cells and stimulate those cells to develop into active bone-forming cells called osteoblasts
- Bone-derived cells to support the osteogenic process. Osteogenesis is the growth of natural bone from preexisting living cells
PRODUCT NUMBERS
DBM
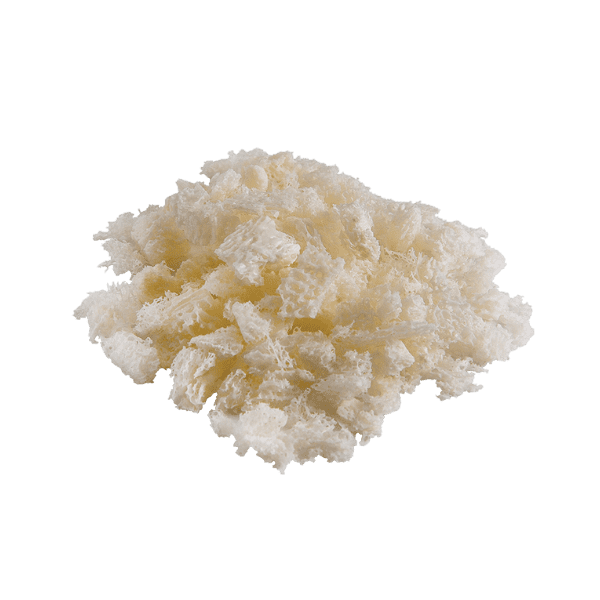
Demineralized bone matrix (DBM) is decalcified allograft bone with osteoinductive potential. The demineralization process exposes growth factors, such as bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP), trapped by minerals. Growth factors recruit immature cells and stimulate those cells to develop into active bone-forming cells called osteoblasts.
PRODUCT NUMBERS
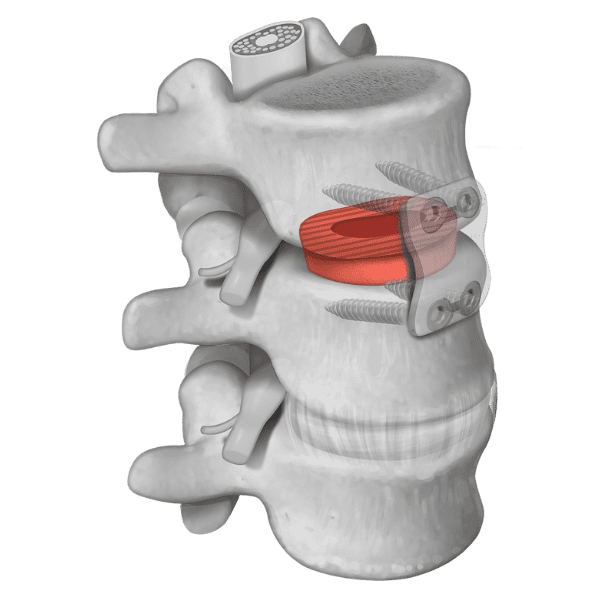
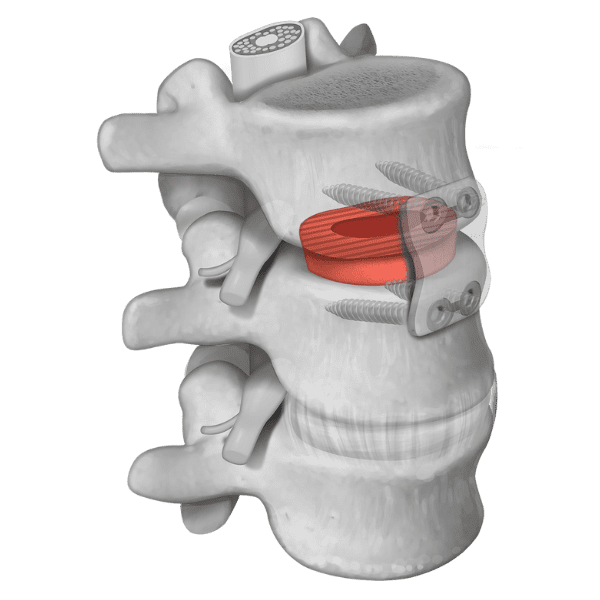
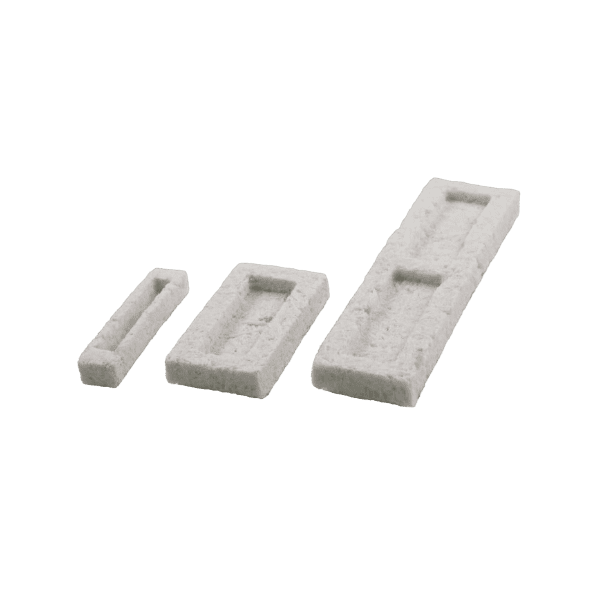
MACHINED SPACERS
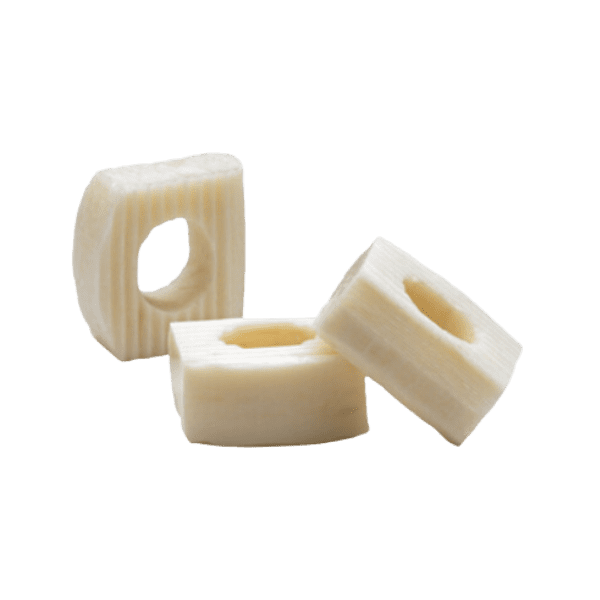
Machined interbody spacers provide a natural osteoconductive option for spine fusion. The allograft bone is precision machined to provide an optimal fit and stability between the allograft and adjacent vertebral bodies. Parametrics Medical offers spacers in various profiles, footprints, and heights.
PRODUCT NUMBERS
SYNTHETIC BONE
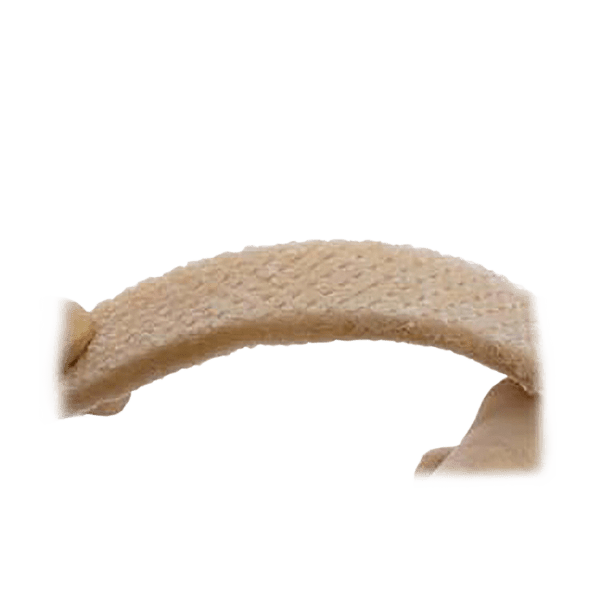
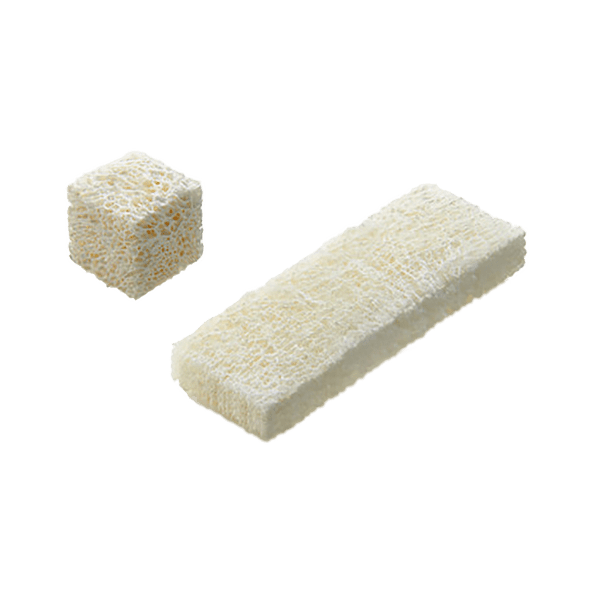
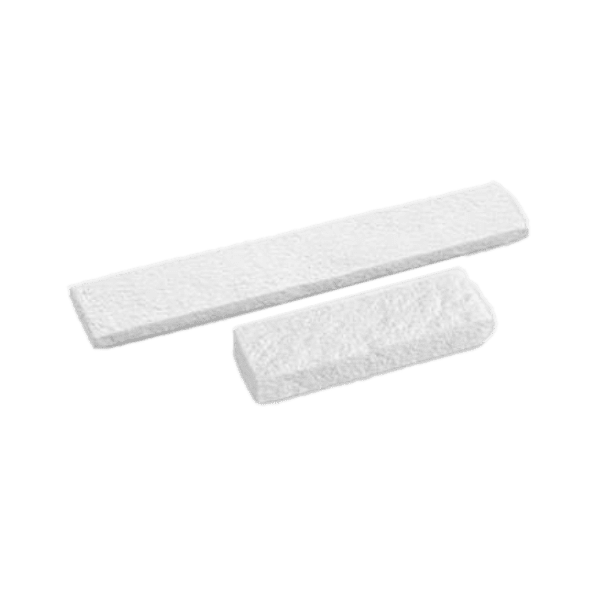
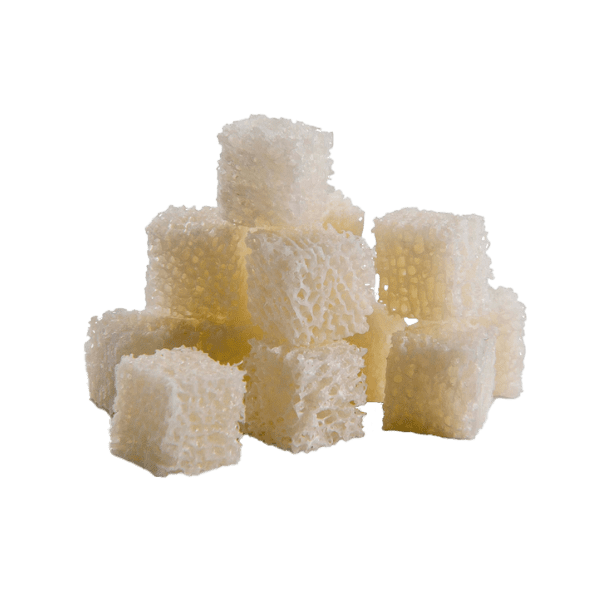
Synthetic bone void fillers are safe, biocompatible, and easy to use. These resorbable biomaterials are based on nano-crystalline hydroxyapatite (HA) and purified collagen technologies. These products are engineered to optimize the resorption rate. Our granules are composed of 60% HA and 40% β-Tricalcium Phosphate (TCP). The formulation provides optimal osteoconduction, and the composition mimics that of human cancellous bone. Our strips are a combination of granules embedded in a fibrillar bovine collagen matrix. Once rehydrated, the foam is flexible. Our bioactive glass foam strips are sterile bone grafts composed of highly purified fibrillar Type I bovine collagen, bioactive glass granules, and HA/TCP granules. It functions as an osteogenic stimulus to which the patient’s bone marrow can be added before implantation.
PRODUCT NUMBERS
VOID FILLING BONE
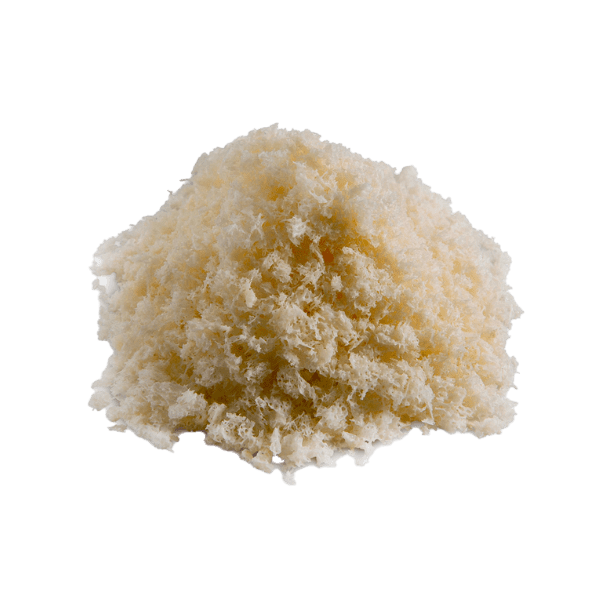
OsteoSource™ allograft bone particulates have osteoconductive properties and are well suited to fill bone structure defects. Osteoconductive allografts act as a scaffold for the growth of natural bone. Over time, the natural bone replaces the donor’s bone. OsteoSource™ eliminates the need for autograft bone, associated with donor site morbidity, longer surgery time, and increased recovery time.
PRODUCT NUMBERS